Section 1 What is Quantum Cryptography
As computers become smarter and faster, these codes become easier to decrypt. That’s why we need to turn to cutting-edge physics to improve encryption. Quantum safe cryptography, a new encryption technology based on the principles of quantum mechanics. Unlike classical cryptography, quantum cryptography relies on physics and does not rely on mathematical operations.
Section 2 Quantum Cryptography and Cryptography historical
Quantum security cryptography originated in cryptography. Today’s cryptosystems are based on keys. The specific algorithms for these encryption methods are public. For example, AES encryption and RSA encryption algorithms are commonly used nowadays. Although there has not been a reliable way to attack the RSA algorithm in the world, this is mainly the current level of computer development. Even if you use the supercomputer of “Sunway TaihuLight” as long as the key length is long enough, you can It is considered unbreakable. However, with the advent of modern quantum computers, the status of asymmetric encryption is also in jeopardy. Because of the computing power, the same size of traditional computers and quantum computers also crack the 1024-bit RSA algorithm, he existing computer may need dozens Ten thousand years, and a quantum computer with 512 qubits can theoretically be cracked within 1 second. Although the number of bits in quantum computers is small now, with the development of technology, in the future, quantum computing will pose a threat to the RSA algorithm.
Therefore, the emergence of quantum cryptography, which is different from classical cryptography, depends on physical principles and does not depend on mathematical operations. Quantum cryptography is based on the “uncertainty principle” of quantum mechanics and the “single quantum non-cloning principle” to ensure that keys are not eavesdropped and eavesdropped. Currently, commonly used methods are called “quantum key distribution,” there are many specific algorithm protocols, such as BB84, BBM92, EKERT91, and so on. The basic principle is through two channels, a quantum channel, and a traditional channel. Quantum channels are used to convey information about quantum states, and classical channels are used to send the necessary information to measure quantum states.
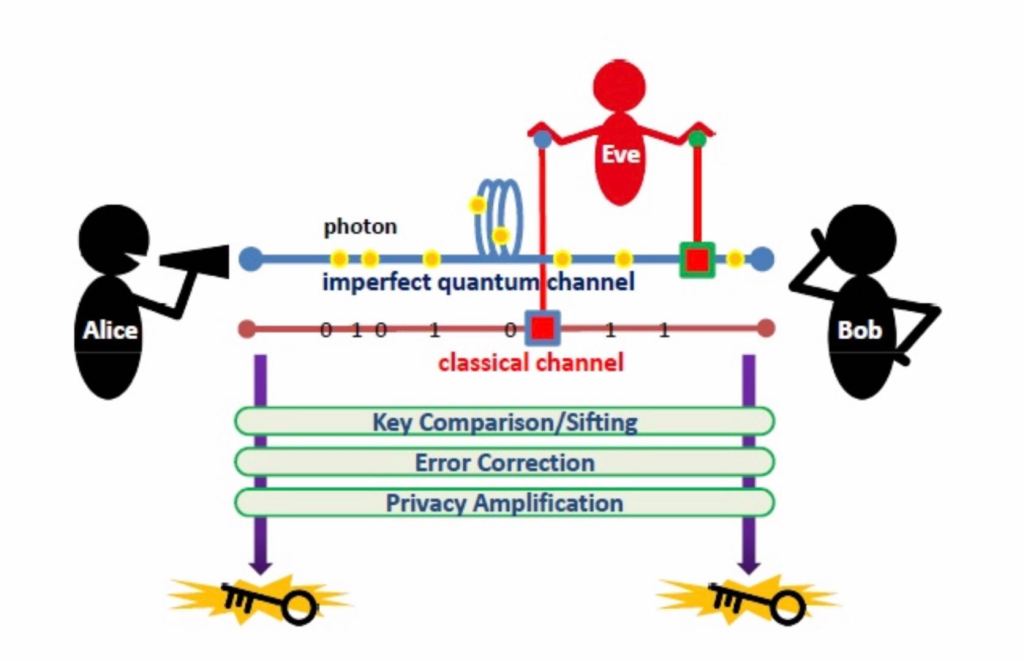
The specific ways are as follows: sender A first transmits quantum state information through the quantum channel, then receiver B conducts random measurement and records measurement method and corresponding measurement result, then A transmits its own measurement method and result through the classical channel, and finally B compares with it. Since B was measured in A random way before, it is necessary to ignore the different measurement methods from A first, and the rest are the same measurement methods, so the results are the same theoretically. If the result is the same, you can think this bit is normal (may not be eavesdropping), if the same results are different measuring ways, that means the middle being measured (must be monitored), the bits can’t be, need to continue to the next set of information, when receive the correct data is enough, can use the collection to the encrypted key. If the eavesdropper avoids direct measurement, such as intercepting or copying the quantum state first, and then transmitting the original quantum state to the receiver B, the replicated quantum state is left for later measurement and analysis, so as to leave no trace in principle. However, quantum has a feature called “single quantum cannot be cloned theorem”, which is a corollary of the “uncertainty principle”, because to copy a single quantum requires measurement, and measurement must change the state of quantum, so there is no way to accurately copy the quantum of an unknown quantum state. Therefore, the quantum encryption method mentioned above is a single quantum scheme, which is also the scheme used by most quantum cryptography technologies at present.
Section 3 Impact of technology
Finally, the emergence of quantum cryptography is more to resist the direct threat of quantum computing to RSA based algorithms. The existing quantum cryptography is not to encrypt data, nor to transmit information through quantum entanglement.
Reference
1.Mahdi H. Al Hasani;Kais A. Al Naimee.Impact security enhancement in chaotic quantum cryptography[J].Optics and Laser Technology,2019,119.
2.Ge Wu;Fuchun Guo;Willy Susilo.Generalized public-key cryptography with tight security[J].Information Sciences,2019,504:561-577.
3. https://i.guancha.cn/news/origin/2019/03/15/20190315084813159.jpg